Why Real-Time Energy Monitoring Matters in Industrial IoT
If you’re in manufacturing, utilities, or any heavy industry, you know energy costs can eat up a huge chunk of your budget. And with rising energy prices and sustainability goals, companies are hunting for smarter ways to track and manage energy consumption. That’s where Industrial IoT (IIoT) energy monitoring steps in as a game changer.
By using connected sensors and smart analytics, IIoT lets you see exactly where, when, and how energy is being used in real-time. This data helps you spot inefficiencies, reduce waste, and make smarter decisions — all leading to big savings and a greener footprint.
But to make this happen, you need the right technical foundation — a solid IIoT architecture designed specifically for real-time energy monitoring.
In this post, we’ll break down the components of an IIoT energy monitoring system, discuss how they work together, and share best practices for building scalable, secure, and efficient solutions.
What Does an IIoT Energy Monitoring Architecture Look Like?
At a high level, your IIoT energy monitoring system consists of these key layers:
 Sensor
Sensor Edge
Edge Communication
Communication Cloud Platform & Data Storage
Cloud Platform & Data Storage Analytics and Visualization
Analytics and Visualization Security and Management
Security and ManagementLet’s dive into each.

Sensor: Capturing Energy Data at the Source
The foundation of any energy monitoring solution is the data — and that starts with sensors.
What Sensors Are Commonly Used?
 Smart Meters
Smart Meters Current Transformers (CTs)
Current Transformers (CTs) Voltage Sensors
Voltage Sensors Power Quality Sensors
Power Quality Sensors Environmental Sensors
Environmental SensorsThese sensors are installed on machinery, transformers, HVAC systems, lighting, and more — wherever you want detailed energy insight.
Key Considerations:
 Accuracy
Accuracy Sampling Rate
Sampling Rate Scalability
Scalability
Edge: Processing Data Close to the Source
Once sensors capture data, it often makes sense to process some of it locally — at the edge — before sending it to the cloud.
Why Use Edge Computing?
 Lower Latency
Lower Latency Reduced Bandwidth
Reduced Bandwidth Improved Reliability
Improved ReliabilityWhat Does the Edge Layer Include?
 Edge Gateways
Edge Gateways Local Compute
Local Compute Protocol Translation
Protocol TranslationFor example, a factory floor might have edge gateways aggregating data from dozens of sensors, running anomaly detection models locally to flag unusual energy spikes.

Communication: Connecting Devices to the Cloud
This layer enables secure, reliable data transmission from edge devices to the cloud or data centers.
Common Communication Protocols and Technologies:
 Wired
Wired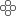 Wireless
WirelessSecurity is Critical: Data encryption, device authentication, and network segmentation protect sensitive energy data during transit.

Cloud Platform & Data Storage: Centralizing Energy Data
The cloud is where all that raw energy data is stored, managed, and prepared for analysis.
Popular cloud platforms supporting IIoT energy monitoring include:
 Amazon Web Services (AWS) IoT
Amazon Web Services (AWS) IoT Google Cloud IoT
Google Cloud IoTThese platforms provide:
 Scalable storage to handle massive volumes of sensor data.
Scalable storage to handle massive volumes of sensor data. Device management to monitor and update connected devices remotely.
Device management to monitor and update connected devices remotely. Data ingestion services that handle various data formats and streaming frequencies.
Data ingestion services that handle various data formats and streaming frequencies.
Analytics and Visualization: Turning Data into Actionable Insights
This is where the magic happens — transforming raw data into dashboards, alerts, and predictive insights.
Typical Capabilities:
 Real-time dashboards showing energy consumption by machine, shift, or location.
Real-time dashboards showing energy consumption by machine, shift, or location. Anomaly detection to spot unusual energy usage patterns indicating faults or inefficiencies.
Anomaly detection to spot unusual energy usage patterns indicating faults or inefficiencies. Predictive analytics to forecast energy demand and plan maintenance schedules.
Predictive analytics to forecast energy demand and plan maintenance schedules. Automated alerts sent via SMS, email, or apps to notify operators of issues.
Automated alerts sent via SMS, email, or apps to notify operators of issues.Visualization tools like Power BI, Tableau, or cloud-native options help stakeholders digest complex data and make informed decisions fast.
Security and Management: Keeping Your IIoT System Safe and Reliable
Security is non-negotiable when dealing with critical infrastructure data.
Key Security Measures:
 Device authentication and authorization to prevent unauthorized access.
Device authentication and authorization to prevent unauthorized access. Data encryption in transit and at rest.
Data encryption in transit and at rest. Network security including VPNs, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems.
Network security including VPNs, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems. Regular patching and firmware updates for all devices.
Regular patching and firmware updates for all devices.Additionally, management platforms provide device health monitoring, logging, and auditing tools to ensure system integrity.
Best Practices for Designing an IIoT Energy Monitoring Architecture
Unlocking Industrial Energy Efficiency with IIoT
Building a robust IIoT architecture for real-time energy monitoring is foundational for any industrial company looking to cut energy costs and improve operational efficiency. By carefully selecting sensors, leveraging edge computing, ensuring secure communications, and harnessing cloud analytics, you can gain unprecedented insight into your energy use — and drive smart, data-driven decisions.
At Infysion, we specialize in designing and deploying custom IIoT architectures tailored to your unique industrial needs. Whether you’re starting your energy monitoring journey or looking to upgrade an existing system, we’re here to help you build scalable, secure, and future-ready IoT solutions.
Ready to speed up your IoT application development with Azure?
Dive into the Azure IoT ecosystem today and start building smarter solutions that transform your business.