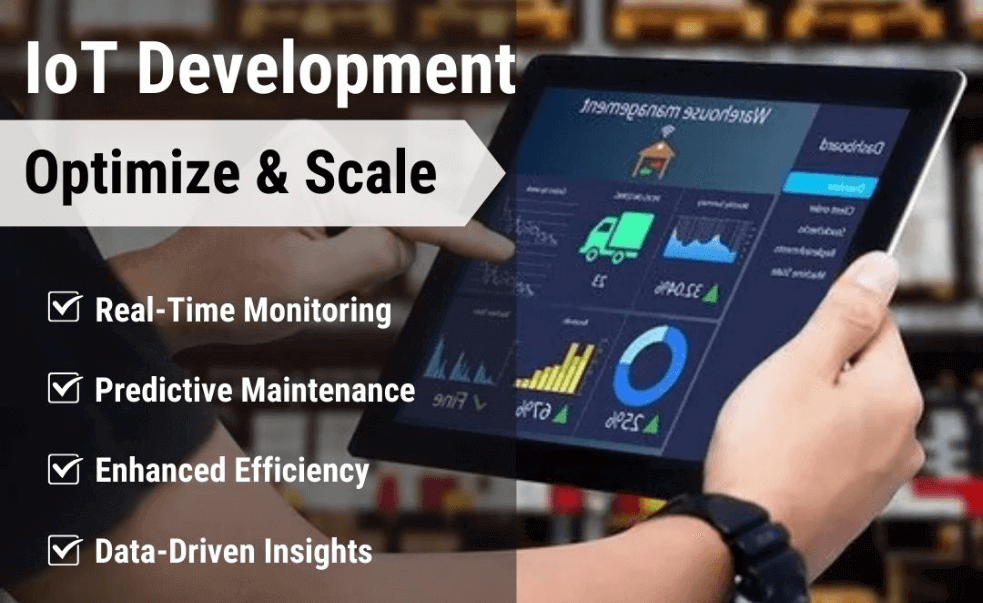
The energy industry is undergoing a digital transformation—and at the heart of it is the Internet of Things (IoT). Whether you’re a utility provider, energy tech innovator, or facility manager, IoT is enabling smarter, more responsive energy systems.
From real-time usage monitoring to automated load balancing, IoT in the energy sector is helping businesses and governments improve sustainability, reduce costs, and increase reliability.
What is IoT in the Energy Sector?
In simple terms, IoT in the energy sector refers to the deployment of connected devices—sensors, smart meters, controllers, and data platforms—that collect and transmit data related to energy production, distribution, and consumption.
These devices can be found in homes, factories, grids, power plants, and renewable installations like solar or wind farms. The real power lies in analyzing this data to make smarter decisions in real-time.
Use Cases of IoT in Energy Management
 Smart Metering and Real-Time Monitoring
Smart Metering and Real-Time MonitoringIoT-enabled smart meters provide precise, real-time data on energy consumption patterns, voltage fluctuations, and load behavior. This helps:
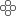 Utilities in dynamic billing and grid management
Utilities in dynamic billing and grid management Consumers in understanding usage and reducing waste
Consumers in understanding usage and reducing wasteExample: A utility company can use IoT data to detect peak usage periods and shift non-critical loads to off-peak times.
 Predictive Maintenance in Power Plants
Predictive Maintenance in Power PlantsWith the help of IoT, grids can autonomously respond to load changes, reroute energy, and isolate faults. This improves the reliability and efficiency of energy distribution.
Example: During high demand, IoT systems can trigger automated power curtailment for non-essential assets, avoiding grid overloads.
 Grid Automation and Demand Response
Grid Automation and Demand ResponseWith the help of IoT, grids can autonomously respond to load changes, reroute energy, and isolate faults. This improves the reliability and efficiency of energy distribution.
Example: During high demand, IoT systems can trigger automated power curtailment for non-essential assets, avoiding grid overloads.
 Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Integration with Renewable Energy SourcesIoT-powered building management systems (BMS) can dynamically control lighting, HVAC, and other systems based on occupancy and weather data.
Example: A smart building reduces energy usage by 30% by adjusting HVAC settings based on indoor air quality and real-time occupancy.
 Smart Buildings and HVAC Automation
Smart Buildings and HVAC AutomationIoT-powered building management systems (BMS) can dynamically control lighting, HVAC, and other systems based on occupancy and weather data.
Example: A smart building reduces energy usage by 30% by adjusting HVAC settings based on indoor air quality and real-time occupancy.
Benefits of IoT in the Energy Sector
 Improved Energy Efficiency: Track and control usage down to the device level.
Improved Energy Efficiency: Track and control usage down to the device level. Lower Operational Costs: Automate maintenance, reduce downtime, and optimize load balancing.
Lower Operational Costs: Automate maintenance, reduce downtime, and optimize load balancing. Grid Reliability: Automated fault detection and remote diagnostics.
Grid Reliability: Automated fault detection and remote diagnostics. Customer Engagement: Real-time insights and personalized energy-saving tips.
Customer Engagement: Real-time insights and personalized energy-saving tips. Sustainability Goals: Reduced carbon footprint with optimized energy use.
Sustainability Goals: Reduced carbon footprint with optimized energy use.Real-World Example: Azure IoT and Smart Energy
Microsoft Azure IoT is being used globally to drive energy innovation.
Example: An energy utility in Europe uses Azure IoT Hub to monitor smart meters in 5 million homes. The solution:
 Gathers telemetry every 15 minutes
Gathers telemetry every 15 minutes Uses Azure Stream Analytics for real-time load predictions
Uses Azure Stream Analytics for real-time load predictions Saves millions in energy distribution and reduces carbon emissions
Saves millions in energy distribution and reduces carbon emissionsChallenges to Consider
 Data Privacy & Cybersecurity
Data Privacy & Cybersecurity Device Interoperability
Device Interoperability Scalability
Scalability Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory ComplianceFuture Trends in IoT for Energy
 AI and ML Integration: Smarter forecasting and autonomous grid behavior.
AI and ML Integration: Smarter forecasting and autonomous grid behavior. Blockchain for Energy Trading: Decentralized, peer-to-peer energy exchanges.
Blockchain for Energy Trading: Decentralized, peer-to-peer energy exchanges. Digital Twins: Simulate grid behavior before implementation.
Digital Twins: Simulate grid behavior before implementation. Edge Computing: Reduced latency and higher security at the edge.
Edge Computing: Reduced latency and higher security at the edge.IoT is not just a buzzword in the energy sector—it’s a game-changer. Whether it’s through optimizing energy consumption, enabling smart grids, or supporting renewables, IoT is paving the way for a smarter, cleaner, and more efficient energy future.
Ready to speed up your IoT application development with Azure?
Dive into the Azure IoT ecosystem today and start building smarter solutions that transform your business.