Water is one of our most critical resources—and yet, it’s one of the most mismanaged. From urban centers to rural infrastructure, aging pipes, manual meter reading, and leakage contribute to billions of gallons of water wasted every year.
Enter IoT-based smart water metering systems. They’re redefining how utilities and municipalities manage water consumption, detect leaks, and ensure sustainability. In this blog, we’re diving deep into how IoT is changing the game for water metering—backed by real-world examples, technical architecture, and future-forward insights.
What is IoT in Smart Water Metering?
IoT in water metering refers to the integration of smart sensors, communication protocols (like NB-IoT or LoRaWAN), cloud-based platforms, and data analytics to collect, monitor, and analyze water usage in real time.
Smart meters equipped with IoT capabilities automatically transmit consumption data, alert for leaks or anomalies, and even shut off supply in emergency situations. This enables utilities to operate more efficiently, bill more accurately, and reduce environmental waste.
Traditional vs. Smart Water Meters: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Meters | Smart IoT-Enabled Meters |
| Reading Method | Manual | Automatic (Remote) |
| Data Frequency | Monthly/Quarterly | Real-time |
| Leak Detection | Not available | Immediate alerts |
| Maintenance | Reactive | Predictive |
| Billing Accuracy | Prone to estimation | Highly accurate |
| Integration | Standalone | Integrated with cloud analytics |
Core Components of an IoT Smart Water Metering System
To understand how these systems work, here’s a look at the main components involved:
 Smart Meters: Digitally record water flow with embedded sensors.
Smart Meters: Digitally record water flow with embedded sensors. Sensors: Flow sensors, pressure sensors, and tamper sensors.
Sensors: Flow sensors, pressure sensors, and tamper sensors. Communication Module: Transmits data via LPWAN (LoRa, NB-IoT), GSM, or RF.
Communication Module: Transmits data via LPWAN (LoRa, NB-IoT), GSM, or RF. Gateway Devices: Aggregate data from meters and transmit to the cloud.
Gateway Devices: Aggregate data from meters and transmit to the cloud. Cloud Platform: Centralized data storage and processing hub (e.g., Azure IoT Hub).
Cloud Platform: Centralized data storage and processing hub (e.g., Azure IoT Hub). Analytics Layer: AI/ML models that forecast usage, detect anomalies, and visualize trends.
Analytics Layer: AI/ML models that forecast usage, detect anomalies, and visualize trends. User Dashboards & Apps: Interfaces for utilities and consumers to access data.
User Dashboards & Apps: Interfaces for utilities and consumers to access data.How IoT is Powering Smart Water Metering: 6 Key Applications
 Real-Time Consumption Monitoring
Real-Time Consumption MonitoringWith real-time tracking, consumers can view their water usage patterns by the hour or minute. Utilities can see aggregated usage by region or zone.
Use Case:
A city municipality integrates LoRaWAN-enabled meters across 50,000 homes. Consumers can track usage via a mobile app, reducing peak-time consumption by 20%.
 Leak Detection & Alerts
Leak Detection & AlertsIoT meters identify unusual consumption spikes and pressure drops that often indicate leaks. Immediate alerts are sent to both the utility and the consumer.
Use Case:
In California, a water utility prevented the loss of 100,000 gallons of water annually using IoT leak detection sensors and automated alerts.
 Automated Billing & Revenue Accuracy
Automated Billing & Revenue AccuracyManual errors and estimated bills are eliminated. IoT systems collect actual usage data, streamlining the billing process and ensuring timely payments.
Use Case:
A utility in Texas reduced billing disputes by 95% after rolling out smart meters across suburban districts.
 Predictive Maintenance
Predictive MaintenanceAI algorithms analyze historical sensor data to predict failures in pipes, valves, or meters—before a breakdown occurs.
Use Case:
Using Azure Machine Learning, an African water authority predicts meter failures 3 days in advance, reducing technician dispatches by 30%.
 Pressure and Flow Monitoring
Pressure and Flow MonitoringMaintaining optimal pressure in distribution lines prevents pipe bursts and ensures service reliability. Sensors continuously monitor this across zones.
Use Case:
In Dubai, real-time pressure sensors help maintain water quality and reduce distribution losses by 12%.
 Remote Valve Operation
Remote Valve OperationUtilities can remotely control valves to shut off supply during maintenance or in case of unauthorized consumption or emergencies.
Use Case:
A European water agency uses remote-controlled smart valves to instantly stop supply in flooded areas, preventing further water damage.
Benefits of IoT in Water Metering for Utilities and End Users
For Utilities:
✅ Reduced operational costs and manual labor
✅ Enhanced demand forecasting
✅ Improved leak detection and water conservation
✅ Regulatory compliance (e.g., non-revenue water management)
For Consumers:
✅ Transparent and real-time usage tracking
✅ Proactive leak notifications
✅ More accurate billing
✅ Mobile access and alerts
Technology Spotlight: Azure IoT for Smart Water Metering
Microsoft Azure offers a scalable platform for utilities to deploy and manage thousands—even millions—of smart meters. Key Azure services used in water metering projects:
 Azure IoT Hub: Device registration and two-way communication
Azure IoT Hub: Device registration and two-way communication Azure Stream Analytics: Real-time flow and pressure data analysis
Azure Stream Analytics: Real-time flow and pressure data analysis Azure Digital Twins: Build a virtual model of water distribution networks
Azure Digital Twins: Build a virtual model of water distribution networks Azure Machine Learning: Leak prediction and pattern detection
Azure Machine Learning: Leak prediction and pattern detection Power BI: Visual dashboards for utility managers and public reports
Power BI: Visual dashboards for utility managers and public reports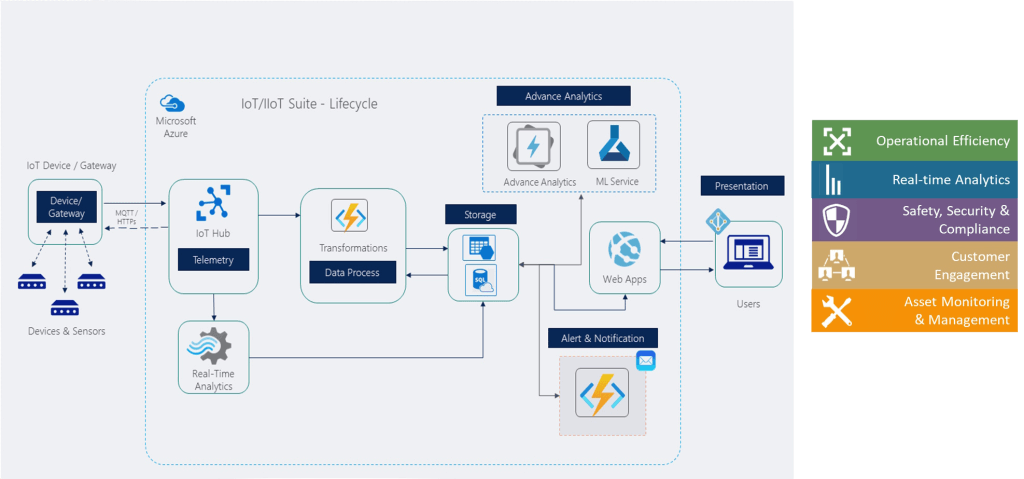
Security and Compliance Considerations
Water systems are considered critical infrastructure—making security a top priority. Key best practices include:
 Data Encryption: TLS and HTTPS between devices and cloud
Data Encryption: TLS and HTTPS between devices and cloud Device Authentication: X.509 certificates or SAS tokens
Device Authentication: X.509 certificates or SAS tokens Firmware Over-The-Air (FOTA): Secure updates for bug fixes and patches
Firmware Over-The-Air (FOTA): Secure updates for bug fixes and patches Compliance: GDPR, ISO/IEC 27001, and local water governance rules
Compliance: GDPR, ISO/IEC 27001, and local water governance rulesReal-World Case Study: Smart Water Grid in India
In Pune, India, the municipal corporation partnered with a technology firm to deploy 100,000 IoT-enabled smart water meters across the city using NB-IoT.
Results:
 Reduced non-revenue water loss by 22%
Reduced non-revenue water loss by 22% Improved billing collection rates by 30%
Improved billing collection rates by 30% Consumers received live consumption alerts via SMS and mobile app
Consumers received live consumption alerts via SMS and mobile appChallenges in Implementing IoT Water Metering Systems
 Initial Cost of Deployment: Smart meters and infrastructure setup can be expensive upfront.
Initial Cost of Deployment: Smart meters and infrastructure setup can be expensive upfront. Connectivity Issues: Remote rural areas may face network reliability issues.
Connectivity Issues: Remote rural areas may face network reliability issues. Data Overload: Managing terabytes of sensor data requires robust backend architecture.
Data Overload: Managing terabytes of sensor data requires robust backend architecture. Resistance to Change: Consumers and utility workers need training and awareness.
Resistance to Change: Consumers and utility workers need training and awareness.Future Trends in IoT and Water Tech
 Edge Computing: On-device analytics for faster response
Edge Computing: On-device analytics for faster response AI-Driven Conservation Tips: Personalized suggestions for water saving
AI-Driven Conservation Tips: Personalized suggestions for water saving Blockchain for Utility Transactions: Transparent billing and auditing
Blockchain for Utility Transactions: Transparent billing and auditing 5G-Enabled Meters: Faster and more reliable data transmission
5G-Enabled Meters: Faster and more reliable data transmissionThe marriage of IoT and water metering is not just about making meters smarter—it’s about making entire cities more efficient, accountable, and sustainable. As climate challenges and urbanization grow, the need for intelligent water management becomes more urgent. Whether you’re a city planner, a utility operator, or a technology partner, now is the time to invest in IoT-enabled smart metering.
Ready to speed up your IoT application development with Azure?
Dive into the Azure IoT ecosystem today and start building smarter solutions that transform your business.