Wastewater treatment is one of the most essential, yet often overlooked, components of urban infrastructure. As cities grow and climate change challenges intensify, efficient wastewater systems are no longer optional—they’re mission-critical.
Enter the Internet of Things (IoT). With real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and remote management, IoT is modernizing wastewater treatment and compliance like never before.
In this blog, we’ll explore how IoT is driving innovation in wastewater management—from smart sensors and AI-driven monitoring to edge computing and Azure-powered dashboards.
What is IoT in Wastewater Management?
IoT in wastewater involves a network of smart sensors, actuators, edge devices, and cloud platforms that monitor and manage water quality, flow, chemical dosing, pump health, and infrastructure conditions in real time.
This integration helps utilities, industries, and municipalities detect issues early, reduce energy usage, and meet environmental compliance with precision and efficiency.
Key Components of an IoT Wastewater Management System
| Component | Function |
| Smart Sensors | Monitor pH, turbidity, TDS, flow rate, ammonia, nitrates, etc. |
| Edge Gateways | Collect and preprocess data near the source |
| Wireless Communication | LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, 4G/5G for data transfer |
| Cloud Platform (e.g., Azure IoT) | Centralized data processing, alerting, visualization |
| Analytics & ML Models | Predictive maintenance, anomaly detection |
| Control Systems | Remotely control valves, pumps, and dosing units |
Real-World Applications of IoT in Wastewater Systems
 Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring
Real-Time Water Quality MonitoringSmart sensors deployed in sewers, pumping stations, and treatment plants can monitor dozens of parameters in real time—pH, COD/BOD, DO (Dissolved Oxygen), turbidity, and more.
Use Case:
A utility in Michigan uses IoT-based turbidity and pH sensors to ensure discharge levels stay within EPA regulations. The system triggers alarms when values deviate from acceptable ranges.
 Predictive Maintenance of Pumps and Equipment
Predictive Maintenance of Pumps and EquipmentIoT sensors measure vibration, motor temperature, and current usage to predict when equipment like pumps and aerators are likely to fail.
Use Case:
An industrial wastewater plant reduced maintenance costs by 40% by using Azure-based machine learning models to detect pump anomalies.
 Overflow and Infiltration Detection
Overflow and Infiltration DetectionDuring heavy rains, combined sewer systems may overflow and discharge untreated sewage. IoT level sensors can predict and alert operators about potential SSOs (Sanitary Sewer Overflows).
Use Case:
A city in Florida installed smart ultrasonic level sensors in sewer manholes. The system sends alerts before overflows, helping avoid fines and environmental damage.
 Chemical Dosing Optimization
Chemical Dosing OptimizationSmart metering and AI analytics can optimize chemical usage (e.g., chlorine, alum, lime) for effective treatment and cost savings.
Use Case:
A treatment plant in the UK used flow sensors and AI to reduce alum dosing by 22% without compromising water quality.
 Remote Monitoring and Control
Remote Monitoring and ControlOperators can view real-time data from decentralized plants or remote pumping stations through a central dashboard, reducing field visits and operational overhead.
Use Case:
An Indian municipality manages 14 remote treatment stations via one control center using Azure IoT Central, reducing manpower cost by 30%.
Benefits of IoT in Wastewater Management
| Benefit | Description |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensure continuous adherence to EPA/local discharge standards |
| Early Fault Detection | Avoid breakdowns and environmental incidents |
| Resource Optimization | Better chemical, energy, and water resource use |
| Operational Visibility | Real-time system-wide insights for proactive decisions |
| Cost Savings | Lower O&M costs through automation and remote management |
| Sustainability | Reduced emissions, waste, and environmental impact |
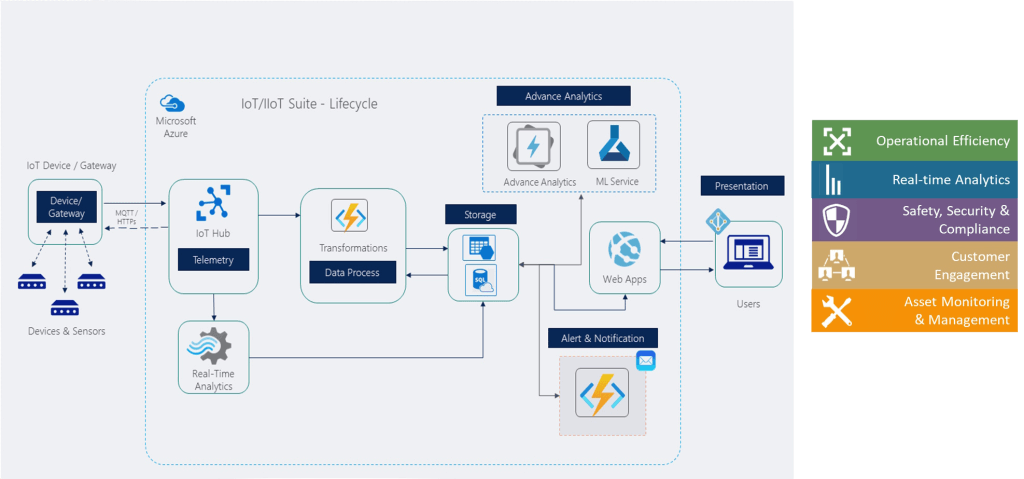
Security Considerations in Wastewater IoT Deployments
Wastewater infrastructure is part of critical national infrastructure (CNI) and demands robust security.
Security Best Practices:
Real-World Case Study: IoT-Enabled STPs in Singapore
Project Summary:
The Singapore Public Utilities Board (PUB) implemented IoT-enabled sensors across 10 sewage treatment plants to improve visibility and efficiency.
Impact:
 Increased plant uptime by 25%
Increased plant uptime by 25% Reduced chemical usage by 18%
Reduced chemical usage by 18% Improved compliance tracking through AI-generated reports
Improved compliance tracking through AI-generated reports Integrated with SCADA systems via Azure IoT Edge
Integrated with SCADA systems via Azure IoT EdgeChallenges in IoT for Wastewater
While the advantages are huge, IoT in wastewater does come with implementation hurdles:
| Challenge | Solution |
| Harsh environment (corrosion, gases) | Use industrial-grade IP68-rated sensors |
| Network connectivity | Use LPWAN (LoRa/NB-IoT) and store-forward methods |
| High upfront costs | Start with high-impact use cases (e.g., predictive maintenance) |
| Data integration with legacy SCADA | Use MQTT bridges and OPC UA adapters |
Future Trends in IoT and Wastewater
 AI-Powered Effluent Forecasting – Predict final effluent quality hours ahead
AI-Powered Effluent Forecasting – Predict final effluent quality hours ahead Digital Twin Models of Treatment Plants – For simulation and planning
Digital Twin Models of Treatment Plants – For simulation and planning Edge AI – Intelligent decision-making directly on-site
Edge AI – Intelligent decision-making directly on-site Green Computing – Energy-efficient IoT processing
Green Computing – Energy-efficient IoT processing 5G-Enabled STPs – Ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and real-time automation
5G-Enabled STPs – Ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and real-time automationFrom aging infrastructure to growing demand and stricter regulations, wastewater management needs a tech upgrade—and IoT is delivering exactly that.
Smart wastewater systems aren’t just about data—they’re about transforming operations, protecting public health, and promoting sustainability. If you’re in the water sector, now is the time to move beyond SCADA and leverage IoT to drive visibility, control, and compliance across your operations.
Ready to speed up your IoT application development with Azure?
Dive into the Azure IoT ecosystem today and start building smarter solutions that transform your business.